Tantalum - The MOST CONFLICT Metal On EARTH!
Thanks for the provided tantalum: http://www.samaterials.com/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/Thoisoi?ty=h
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/thoisoi2
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/thoisoi/
Do not repeat the experiments shown in this video!
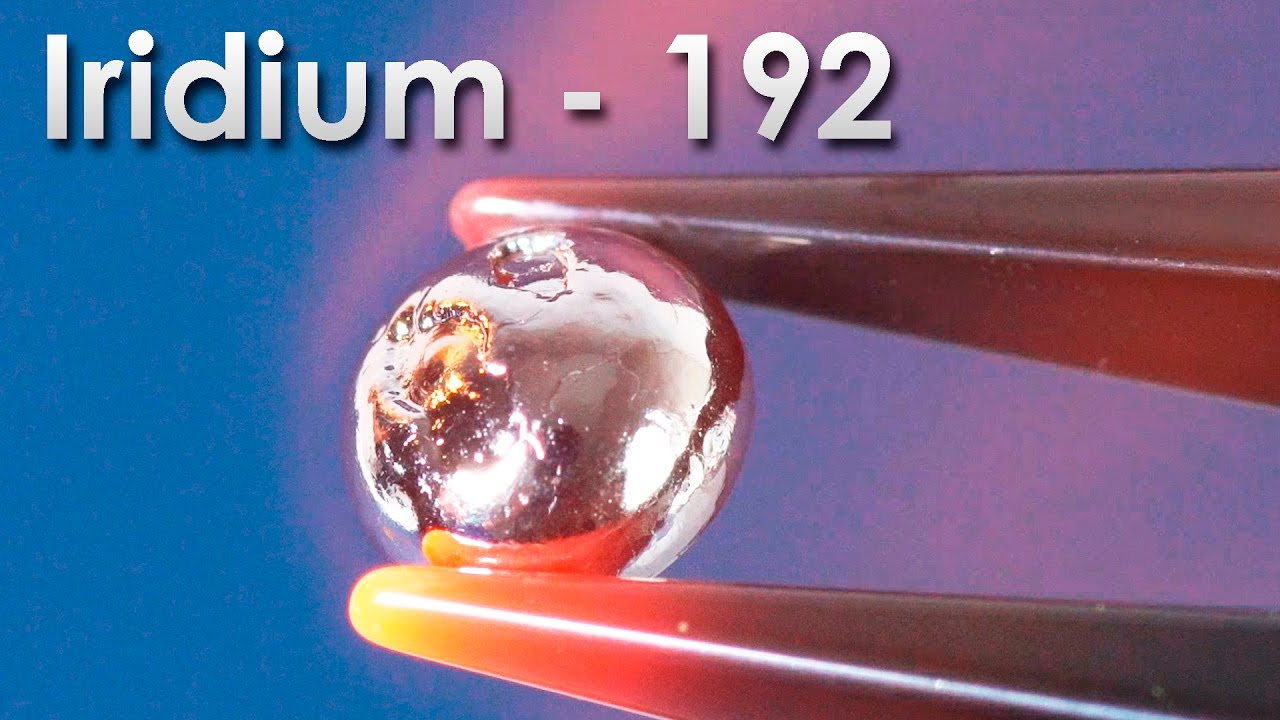
So, today I want to tell you about this refractory and also a conflict making metal, tantalum. In the periodic table of chemical elements tantalum is located in the fifth group, among the so-called transitional refractory metals.
Due to its rarity and difficulty in obtaining, tantalum was named after the Greek king Tantalus. According to the legend, he offended Zeus and the other gods, for which he was cast out of heaven for an eternal torment. Like the ancient Greek king, many scientists and researchers have suffered and endured, trying to obtain this element in its pure form. Externally, tantalum looks like a grey shiny metal, and by the way quite heavy. In its density it comes next after the gold. If you take the current market price, one kilogram of tantalum costs around $150, therefore this metal is quite expensive.
Tantalum is very ductile, it’s very easy to make a wire or foil from it. This metal is extracted from the mineral coltan, the deposits of which are located in Brazil, but especially rich deposits of tantalum ores are found in Central Africa.
Recently tantalum is referred to as a conflict making metal, because a lot of African countries are fighting to get their hands on it. For example, in Congo and Rwanda there are military conflicts associated with the smuggling of tantalum ore. From about the last decade, about 9 African countries and 20 different military groups were involved in the tantalum wars. However, let’s go back to the chemical properties of the tantalum metal. From the chemical point of view, this metal is extremely stable, it is not soluble in dilute acids, even in the hydrofluoric acid due to a very robust oxide film covering the metal. One of the very few caustic environments that can dissolve tantalum is a mixture of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, in which from the tantalum a complex compound forms that is soluble in water. In the form of a powder tantalum burns quite well in air, forming the tantalum oxide. In spite of all its chemical stability, this metal also reacts well with molten alkalis, forming tantalates.
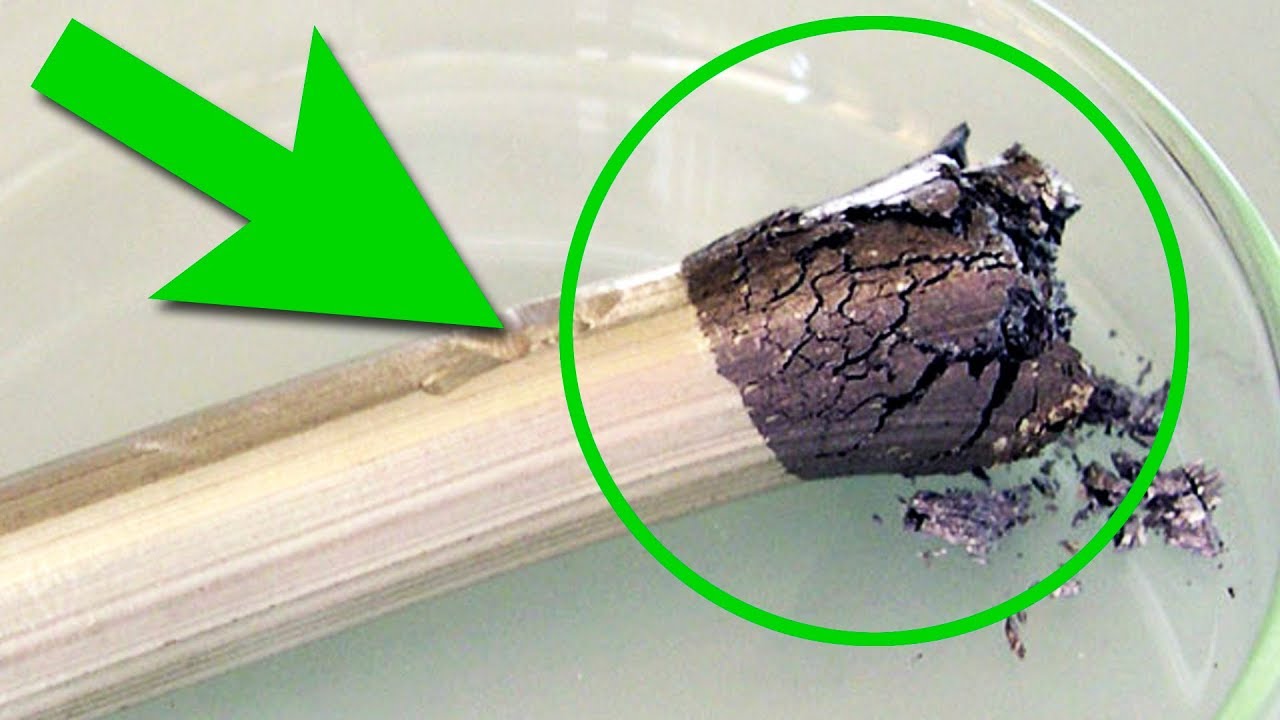
For example, if you pour a bit of dry sodium hydroxide on the tantalum foil and then melt it, such an aggressive environment can easily dissolve the tantalum and burn a hole in the tantalum foil. Though that’s pretty much it, you cannot conduct any other special chemical experiments with tantalum due to its inertness. The only thing we can do is heat the tantalum rod and see how fast will it oxidize in the hot flame of a gas burner. After such an abuse, tantalum rod gets covered with a white and inert substance – tantalum oxide from reacting with oxygen in air. This material is also used in creating glass that absorbs gamma rays.
Because of its plasticity and chemical stability, in the olden days tantalum was used for making filaments for light bulbs, but later with the rise of the price for this metal, tantalum was replaced with a much cheaper tungsten. The internal resistivity of tantalum is comparable to the one of steel, hence this element can be used to create heating elements instead of using nichrome, especially in places where you need a very high temperature, as tantalum melts at more or less about three thousand degrees Celsius! So, for example, it is possible to heat the tantalum wire and it will not oxidize as much. At the moment, one of the most important applications of tantalum is in manufacturing the most efficient tantalum capacitors, in electronics. In the capacitors like anode a very fine tantalum powder is used, which is pressed around the tantalum wire and is sintered to the form of a sponge. Then such sponge is anodized, i.e. is covered with a layer of tantalum pentoxide that acts as the dielectric layer. Next, the anodized tantalum sponge is covered with a layer of the cathode of manganese dioxide. Then, on top, a layer of graphite and a layer of silver is added, and now the capacitor is ready. The advantage of these capacitors is that they can be made to be extremely small, due to the very thin dielectric film. These kind of capacitors can be put into any computer, smartphone or a tablet. So say thanks to tantalum for the smartphones. Recently, jewelers are trying to use tantalum in the jewelry, as this metal is quite dense and is completely non-toxic to humans. Now even the Chinese sell tantalum rings. Hmm, would you gift your girlfriend a tantalum decoration? In my opinion, it would be quite original. However, tantalum by itself is grey and doesn’t shine as beautifully as gold.